Lyme behandeling
In het kort: Doxycyline
helpt tegen de spirocheten vorm van Borrelia maar deze zet
zichzelf om in de cyste vorm.
Samento en Banderol
bestrijden de andere vormen zoals de cyste en de biofilm.
Doxycyline doet dat niet.
Samento verkleint de
biofilm kolonies aanzienlijk, maar dood deze niet.
Banderol verkleint de
kolonies niet maar dood deze tot wel voor 90%
Samento en Banderol
samen werkt beter.
Doxycycline samen met
andere antibiotica werkt toch sneller op de duur. Samen met
het Cowden protocol zal dit het beste resultaat haalbaar
geven.
Lyme treatment
Abstract
A tick-borne, multisystemic
disease, Lyme borreliosis caused by the spirochete Borrelia
burgdorferi has grown into a major public health problem
during the last 10 years. The primary treatment for chronic
Lyme disease is administration of various antibiotics.
However, relapse often occurs when antibiotic treatment is
discontinued. One possible explanation for this is that B.
burgdorferi become resistant to antibiotic treatment, by
converting from their vegetative spirochete form into
different round bodies and/or into biofilmlike colonies.
There is an urgent need to find novel therapeutic agents
that can eliminate all these different morphologies of B.
burgdorferi. In this study, two herbal extracts, Samento and
Banderol, as well as doxycycline (one of the primary
antibiotics for Lyme disease treatment) were tested for
their in vitro effectiveness on several of the different
morphological forms of B. burgdorferi (spirochetes, round
bodies, and biofilmlike colonies) using fluorescent,
darkfield microscopic, and BacLight viability staining
methods. Our results demonstrated that both herbal agents,
but not doxycycline, had very significant effects on all
forms of B. burgdorferi, especially when used in
combination, suggesting that herbal agents could provide an
effective therapeutic approach for Lyme disease patients.
Borrelia burgdorferi, the primary
causative agent of Lyme disease, is a spirochetal bacterium that
can adopt different inactive forms, such as cystic and granular
forms (round bodies), as well as colonylike aggregates both in
vivo and in vitro, in the presence of unfavorable conditions
such as exposure to the antibiotics commonly used for treating
Lyme borreliosis.1-4 Unfortunately, when B.
burgdorferi is in these inactive forms, conventional antibiotic
therapy will not destroy the bacteria.3 Still to
date, the frontline treatment for Lyme disease is administration
of pharmaceutical antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline,
clarithromycin, penicillin G, and ceftriaxone.4,5
Many studies have shown that in spite of continued and high-dose
antibiotic therapy, chronic Lyme disease is not treated
successfully in many cases.6 Also, in the absence of
ongoing antibiotic treatment, relapse is common.7,8
This means that even after antibiotic treatment, the host
immunity fails to prevent recurrence.8 One possible
explanation for this clinical observation is the presence of
different morphological forms of B. burgdorferi, which
mayprotect it from the antibacterial therapy. Soon after
treatment, relapse is observed, most likely because the B.
burgdorferi can revert to the spirochetal form. Furthermore, the
cost of antibiotic treatment, especially when administered
intravenously, is substantial. Antibiotic therapy may also cause
multiple undesirable side effects.9 Thus, there is an
urgent need for novel, more efficient, and more cost-effective
treatment approaches that can efficiently eliminate all forms of
B. burgdorferi.
There is an alternative clinical treatment option gaining wide
use, called Cowden Condensed Support Program, that utilizes
several herbal extracts designed to eliminate microbes in Lyme
disease patients. Richard Horowitz, MD, president of the
International Lyme and Associated Diseases Educational
Foundation (ILADEF), has prescribed this protocol for over 2000
of his patient and reports that it has been effective for more
than 70% of them. The two herbal agents from the Cowden
Condensed Support Program selected for this study are Samento (a
pentacyclic chemotype of Cat's Claw [Uncaria tomentosa] that
does not contain tetracyclic oxindole alkaloids), with reported
antibacterial and antiviral properties, and Banderol (Otoba
sp.), known to have antibacterial, antiprotozoal and
anti-inflammatory effects.10-12 Both herbal agents
are used during the first two months of Cowden Condensed Support
Program, then in rotation with other antimicrobials for the
duration of this 6-month protocol.
In this study, we evaluated these natural antimicrobial herbal
extracts as well as doxycycline (one of the primary
pharmaceutical antibiotics for Lyme disease treatment) for their
potential effects on the different forms of B. burgdorferi.
The infectious B31strain of B. burgdorferi used in this study,
obtained from American Type Tissue Collection(ATCC# 35210), was
culturedin 5% CO2 at 34 oC, in Barbour–Stoener–Kelly H (BSK H)
medium supplemented with 6% rabbit serum (Sigma, St. Louis,
Missouri) to midlogarithmic stage (2 × 107 cells/ml). Samento
and Banderol were obtained from Nutramedix LLC (Jupiter,
Florida). Doxycycline was obtained from Sigma. A wide range of
concentrations of Samento and Banderol were initially tested to
determine the effective concentrations (1:100–1:1000 dilutions).
For doxycycline, a concentration 10× higher than the reported
minimum bactericidal concentration (250 µg/ml) was used.13
Triplicate test tubes containing BSK H medium, with and without
the appropriately diluted antimicrobial agents, were inoculated
with a final density of 5 × 106 cells/ml of the test organism.
Direct cell counting methods with Petroff-Hausser counting
chambers and morphological studies using fluorescent and
darkfield microscopic techniques, as well as LIVE/DEAD BacLight
Bacterial Viability Assay (Life Technologies Corp, Carlsbad,
California), were utilized to assess the effect of the
antimicrobial agents. For statistical analyses, one sample
paired T-test was performed using NCSS statistical software (NCSS
LLC, Kaysville, Utah).
Samento
& Banderol Herbal Extracts
Figure 1A Samento vs Doxycycline
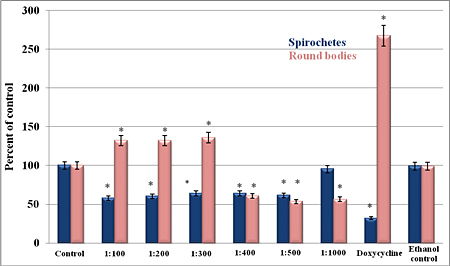
Figure 1B Banderol
vs Doxycycline
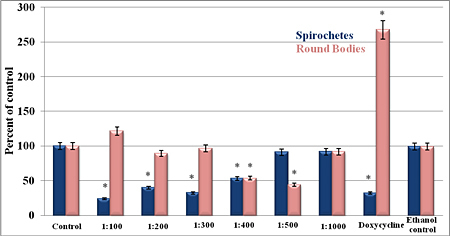
Figure 1C
Samento and Banderol vs Doxycycline
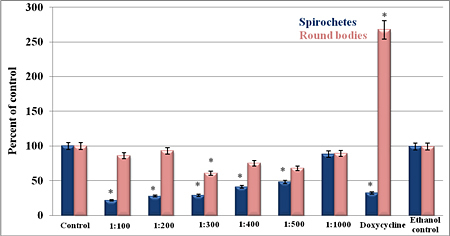
Figures
1: The in vitro
susceptibility of the spirochete and round-body forms of the B31
B. burgdorferi to Samento and Banderol extracts and to
doxycycline (250 µg/ml) for 96 hours' treatment period using
direct cell counting and darkfield morphological evaluation
methods. (A) Samento extract; (B) Banderol extract; (C) Samento
+ Banderol extracts. As a negative control, 0.25% ethanol was a
used. *P- values >0.05 indicates statistical significance.

In the first set of
experiments, we tested the in vitro susceptibility of the
spirochete and round-body forms of the B. burgdorferi B31 strain
to Samento and Banderol extracts for 96 hours, then direct cell
counting and darkfield morphological evaluation methods were
used to measure the effects of the antimicrobial agents. For
both herbal extracts, the dilution of 1:400 most efficiently
eliminated both the spirochetal and round-body forms (Figure 1A
and 1B). However, when we used the combination of Samento and
Banderol extracts, 1:300 dilution showed the most effectiveness,
and this concentration was chosen for further study (Figure 1C).
As a negative control, 0.25% ethanol treatment was also included
in all experiments, because these herbal extracts contain ~25%
ethanol to transport the nutrients into the cells and for
stability.
In these experiments, we also
compared the effect of Samento and Banderol with doxycycline,
the most common antibiotic treatment agent for Lyme disease
treatment in a 96-hour treatment period. Our results showed that
doxycycline (250 µg/ml) was very effective in eliminating the
spirochetal form of B. burgdorferi, but it significantly
increased the round-body forms. Comparing this doxycycline data
with that of the herbal extracts, Banderol and the combination
of Samento and Banderol (1:300) were more efficient in
eliminating both the spirochetal and round-body forms of B.
burgdorferi in vitro (Figures 1A–C).
In the next set of
experiments, we evaluated the effect of the different
antimicrobial agents on biofilmlike colonies of B. burgdorferi.
The cultures were treated as described above for 96 hours and
stained with BacLight fluorescent viability stains, which can
help visualize the effects of the antimicrobial agents on the
bacterial cells (Figure 2). The green fluorescent stain (SYTO 9,
with excitation/emission maxima of about 480/500 nm) colors
healthy bacteria that have intact membranes, thus staining live
cells; and the red dye (propidium iodide with
excitation/emission maxima of about 490/635 nm) colors bacteria
with damaged membranes, by displacing the green dye, thus
staining dead cells.

Figures
2: BacLight viability
staining of B31 strain of B. burgdorferi after 96-hour treatment
using SYTO 9 green-fluorescent nucleic acid stain (live cells)
and propidium iodide, a red-fluorescent nucleic acid stain (dead
cells). (A) Control; (B) Samento (1:300 dilution); (C) Banderol
(1:300 dilution); (D) Samento + Banderol (1:300 dilution); (E)
Doxycycline (250 µg/ml). All images are taken at 40×
magnification.
Figure 2A Biofilm:
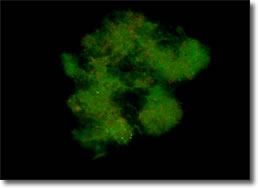
Figure 2B Biofilm after Samento:
Much smaller colonies:
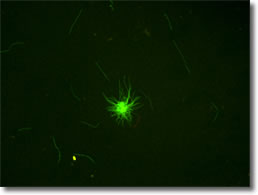
Figure 2C Biofilm after
Banderol: Colonies not smaller but >90% dead.
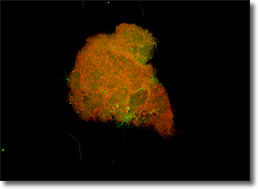
Figure 2D Biofilm after Samento
and Banderol:
Only
a few individual nonmotile but green spirochetes and
round bodies are left over.
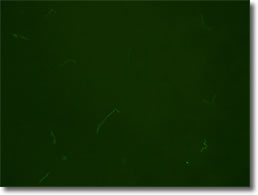 |
In the absence of
antimicrobial agents, B. burgdorferi is forming
biofilmlike colonies (Figure 2A) with mainly live
bacterial cells.
In the presence of Samento extract
(1:300), the colonies were significantly smaller and
less organized (Figure 2B), but they did stain with
green dye, indicating that live cells remained.
In the
presence of Banderol extracts, the size of colonies did
not show any reduction; however, the cells inside the
colonies are >90% dead.
In the presence of both
herbal extracts, no sign of any colony formation was
observed in the cultures, but we found evidence of a few
individual nonmotile but green spirochetes and round
bodies. In the presence of doxycycline (250 µg/ml), the
average colony size was increased and contained mainly
live round-body forms.
Here we have
provided evidence that two natural antimicrobial agents
(Samento and Banderol extracts) had significant effect
on all three known forms of B. burgdorferi bacteria in
vitro
In this study, our
working hypothesis was that for an efficient therapy, we
have to find antimicrobial agents that can eliminate all
the forms of B. burgdorferi. During the course of
Borrelia infection, the bacteriumcan shift among the
different forms, converting from the spirochete form to
the others when presented with an unfavorable
environment and reverting to the spirochete when the
condition is again favorable for growth.1-4
To successfully eradicate B. burgdorferi, antimicrobial
agents should eliminate all those forms, including the
spirochetes, round bodies, and biofilmlike colonies.
|
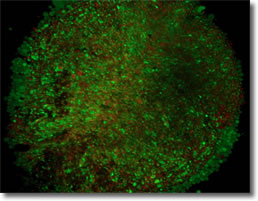
Figure 2E
Doxycycline:
Decreased spirochetal form but increased round body
number.
|
We have also demonstrated that doxycycline, one
of the primary antibiotics used in the clinic to treat
Lyme disease, only had significant effect on the
spirochetal form of B. burgdorferi.
|
Our later results might provide some
explanation for why relapse is so common after discontinuing
antibiotic therapy. For example, some of the recent reports on
animal experiments demonstrated that although pharmaceutical
antibiotics are effective in ameliorating disease, the infection
may persist even after seemingly effective therapy, which
suggested that Borrelia may remain viable even after antibiotic
administration.14-15 If those pharmaceutical
antibiotics only eliminate one form of this bacterium, the other
forms could be the source of the persistent disease.
The other very important fact needs to be considered for an
effective treatment for Borrelia infection: this bacterium
typically has a life span ranging from several weeks to six to
eight months; therefore, it may take six to eight months for
even one generation of Borrelia to become exposed to the
antimicrobial for elimination.16 Since the herbal
extracts like Samento are reported to be nontoxic, they can be
safely taken daily for the long period of time necessary to
thoroughly eradicate Borrelia from an infected body.17
In summary, our study has provided in vitro research data on a
novel treatment approach using herbal antimicrobial agents to
efficiently eradicate B. burgdorferi, the Lyme disease
bacterium.

Corresponding
Author
Eva Sapi, PhD
University of New Haven
Middelen die werken bij Lyme:
Samento
is very effective against Borrelia
Banderol
is very effective against Borrelia
Cumanda
is very effective against Borrelia
Quina
very effective in treating Borrelia en
ook voor
chlamydia
pneunomia
Lakato
is very effective against Borrelia burgdorferi.
En chlamydia pneunomia.
Serrapeptase voor het verwijderen van laag om lyme bacteriën en
het schoonmaken van aderen en het toegankelijk maken van weefsel
om de aderen.
Burbur
detox
Babuna gelijk effect aan diazepam op slaap
Amantilla
gelijk effect aan diazepam op slaap
Maar nu weer met beide
benen op
de grond:
"Cowden
werkt prima, alleen geeft 6 maanden antibiotica het hetzelfde
resultaat als 12 tot 18 maanden cowden" Carsten Nicolaus.
Carsten Nicolaus
VIDEO
Carsten Nicolaus
na 44 minuten over cowden.
BCA test na 9 maanden cowden evaluatie.
Cowden programma heeft bewezen zeer succesvol te zijn.
Alleen geeft 6 maanden antibiotica het
hetzelfde resultaat als 12 tot 18 maanden cowden.
chlamydia pneunomia in 85 % van de
mensen met Lyme
30 tot 35 procent van de mensen met
borellia burgdorferi hebben ook bartonella.
20 tot 30% heeft ook ehrlichia naast
bb
Mycoplasma 50 - 60% van mensen met
lyme.
80 tot 90 % van de teken heeft babesia.
Cowden en antibiotica kunnen prima
tegelijk worden toegepast.
chlamydia geeft vaak borstpijn.
Dr. Armin Schwarzbach
Video Dr.
Armin Schwarzbach
Spirostat lab texas test op 10 tallen spirochettes en microbes
with ultrasensitive pcr
Dr Lee Cowden:
Video Dr
Lee Cowden
Patient op Samento. Na 2 weken veel
minder spirochettes in het bloed na 4 weken 0. Maar nog steeds
klachten. Dan bleek in de rode bloedcellen ook de lyme te zitten.
Maar na weer 2 weken waren het er veel minder, na4 weken waren
deze ook geheel weg. lee cowden na 20 minuten.
Herxheimer: te veel dode bacteriën
stapelen op in de weefsels. Dat geeft een vergiftiging in de
weefsels. Geeft hoofdpijn, duizeligheid, voamitting, spierpijn,
gewrichtspijn. Met drainage therapie gaat dit meestal met 1 tot
3 uur weer over.
Toch behandel duur van 1 jaar met
cowden volgens cowden zelf.
na 18 weken 50 -75% verbetering. 78
dag... patient... op samento en banderol. 190, dagen behandeling
Met serrapeptase reinigen van de bloedvaten. Het haalt de vezels
weg die de microbes bedekken. Het lichaam bedekt de microbes om
te zorgen dat de microbes het lichaam niet beschadigen. Maar
daarmee kan het immuunsysteem de microbe ook niet meer zien en
aanvallen. En daarmee wordt ook de binnenkant van de bloedvaten
bedekt en deels afgesloten. De doorgeeftijd van zuurstof kan
teruggelopen zijn van 5 seconden naar 5 minuten. Dat is 60x
langzamer.
Inname 30 minuten voor het eten met water.
Banderol werkt tegen de bacterien en samento remt het
immuunsysteem om niet over te reageren.
Om de 12.5 dagen 36 uur geen banderol
etc nemen zodat de spirochette vorm weer terug komt en goed ook
door de antibiotica weggehaald kan worden. De spirochette vorm
is erg kwetsbaar voor de antiherbals en antibiotica. Alle
stoffen naar 2 maal per dag 30 druppels.
verder na 78 dagen van samento naar
cumanda en dan naar houttuynia en weer terug.
Enige leuke weetjes over Borrelia:
Borrelia bestaat al meer dan 20 miljoen jaar. De bacterie is
gevonden in 20 miljoen jaar oude boomhars. Daarmee is het ouder
dan de mensheid zeld, deze is ongeveer 5 miljoen jaar geleden
begonnen.
Borrelia is bijzonder langzaam: De delingstijd van een
gemiddelde bacterie is enkele minuten. Borrelia deel tussen de 3
weken en 8 maanden. De antibiotica heeft alleen een werkingskans
op het moment van delen. Daarom duurt een behandeling ook lang.
Chronische Lyme is moeilijk te meten. De standaard metingen
meten de reactie van het lichaam. Bij chronische Lyme is de
reactie van het lichaam door de Borrelia juist onderdrukt. Dan
moet eerst langere tijd antibiotica gebruikt worden zodat het
lichaam weer kan reageren en er dus een reactie meetbaar is.
Daar begin je natuurlijk niet aan als je om te beginnen geen
reactie meet...
Borrelia houdt vooral van bindweefsel.
De bacteria communiceren met elkaar om elkaar te leren wat ze
moeten doen tegen aanvallen door het lichaam.
|







